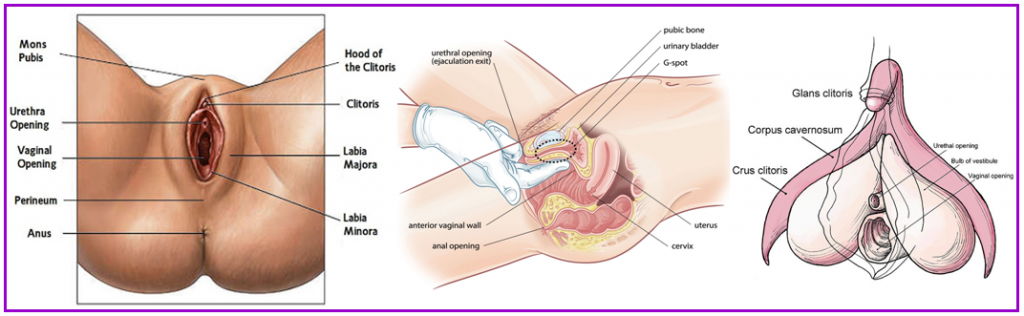
It is surprising how many women have not taken the time to get to know what their own sexual parts look like or what they are called and very few have accessed to information on what female sexual parts are and how these parts can increase sexual responsiveness. Female sexual anatomy can be broken down into two categories, external and internal.
External Genitals
- Vulva: The vulva refers to the most visible parts of the female genitals and includes the Mons Pubis (pubic mound), outer and inner labia, clitoral hood, urethral opening and vaginal opening. The look of the vulva varies from woman to woman in size, shape and color.
- Mons Pubis: Also called the Mons Veneris or ‘Mountain of Venus’, this is the area of skin that lies above the pubic bone. It is often rounded with a fatty pad of tissue under the skin and is where most of the pubic hair grows. It may be the least sensitive part of the vulva but many women enjoy the feeling of touching, massage or even vibration, as the stimulation can be felt throughout the area.
- Labia: Latin for “lips”, women have two sets of labia. The outer thicker labia, called Labia Majora, are what you see without spreading your legs wide open. In between the Labia Majora are another set of lips, the Labia Minora (“little lips”). These are much thinner and more flexible than the Labia Majora. The inner labia may be longer or seem to stick out more than the outer labia and tend to be more sensitive to stimulation.
- Perineum: This is the area between the vaginal opening and the anus. During sexual arousal and excitement, the area may become more sensitive and some women may find massaging the area to be pleasurable where others may find it too sensitive for direct stimulation.
- Clitoris & Clitoral Body: The labia come together at the top into a little hood that covers the clitoris. The visible part of the clitoris sits under the top of the Labia Minora; this tip is made mainly of erectile tissues. These tissues become engorged with blood during arousal making it firmer and larger. This area can be highly sensitive & pleasurable and contains 8,000 nerve endings, double the amount of the male glans. What you won’t be able to directly feel or see is the clitoral legs that extend inside the body into two roots on either side of the vagina.
- Urethral Opening: The urethral opening is where urine comes out and can be seen if you pull back the folds of the labia. Some women find stimulation of this area to be very pleasurable, some don’t notice and others find stimulation irritating.
Internal Sexual Anatomy
- The Vagina: Located between the vaginal opening and the cervix. The vagina has both reproductive and sexual pleasure functions and capacities. There’s no ideal size or shape to a vagina and the size changes dramatically as a woman becomes aroused. For most women, the vagina is self-lubricating and usually moist on the inside. The bottom/outermost third of the vagina has the most nerve endings and is the most sensitive to stimulation. The upper two-thirds of the vagina have relatively few nerve endings, and most women will only feel sensation from deep pressure. The vagina is on an angle in the body, tilting slightly backward from bottom to top with the cervix at the top. Most women find touching the cervix to be uncomfortable and/or painful, although a select few may enjoy the feeling.
- Urethral Sponge or G-spot: A number of glands surround the area between the bladder and the urethral opening. Fluid is produced in these glands and may be released into the urethra during orgasm. Some women produce a noticeable amount of lubrication, even to the extent similar to ejaculation. Many find that they have a sensitive spot on the inside and top of the vaginal wall that can be felt and swells when stimulated, this is known as the G-spot. For more information see our G-spot pamphlets.
- PC Muscle: The PC muscle, pubococcygeus muscle, is a sling of muscles that support the pelvic floor and surround the internal genitalia. These muscles are involved in urination (when you stop yourself from peeing in mid-stream, you’re using your PC muscles) and are also involved in orgasm. Many women find that doing regular exercises to strengthen these muscles changes the way their sexual response feels. These exercises are usually referred to as kegel exercises and can be enhanced by using kegel (Ben Wa) balls or weights.
- Hymen: The hymen is a thin membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening inside. Contrary to much mythology, the hymen is not a solid structure that is broken (or “popped”) during first vaginal penetration. The hymen usually has several openings and may change and stretch as a woman’s body changes through puberty.
- Uterus: Located above the cervix, the uterus or “womb” is a hollow, muscular organ in which a fertilized egg becomes embedded and nourished as it develops until birth. It lies in the pelvic cavity above the cervix.
We hope this helps increase your understanding of the female pleasure system and helps you discover new types of satisfaction!

